2025-05-01 https://www.aluminum-coils.com/a/aluminum-plate-sheet.html
The Unsung Hero of Modern Manufacturing: A Deep Dive into Aluminum Plate Sheets
In the vast world of metal fabrication, the aluminum plate sheet occupies a uniquely versatile and indispensable niche. While often overshadowed by steel or specialty alloys, aluminum plates are the silent workhorse driving innovations across industries, from aerospace to automotive, construction to consumer electronics. aluminum plate sheets from a distinct technical and industrial perspective reveals why this material remains a cornerstone in modern manufacturing.
What Makes Aluminum Plate Sheet Exceptional?
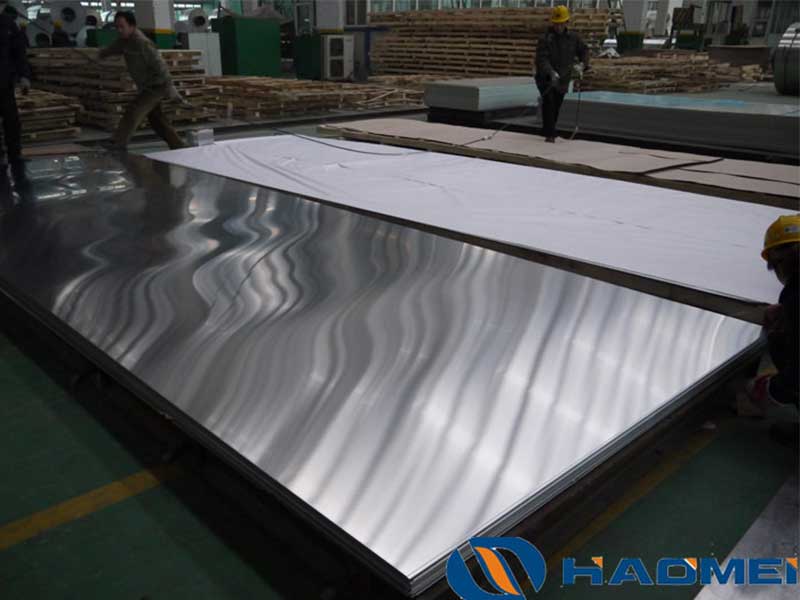
At its core, aluminum plate sheets differ from aluminum foil or coils primarily in thickness, typically starting from 6mm (about 0.25 inches) and extending up to several inches, depending on the required application. This dimensional characteristic opens up a wide array of structural and lightweight design possibilities.
However, the true uniqueness of aluminum plate sheets lies in their combination of mechanical properties and formability, derived from how alloys and processing methods intersect:
-
Alloy Composition: Lightweight aluminum alloys such as 5000 and 6000 series are usually preferred for plate sheets. The 5000 series features magnesium as the primary alloying element, enhancing corrosion resistance, ideal for marine environments and architectural cladding. The 6000 series incorporates magnesium and silicon, balancing strength with excellent machinability, commonly found in transportation and heavy machinery.
-
Heat Treatment and Temper: The structural properties of aluminum plates can be finely tuned through heat treatments such as annealing (O temper), strain hardening (H temper), or solution heat treatment followed by aging (T temper). Plates with T6 temper, for example, show an optimized balance between tensile strength and corrosion resistance, lending themselves well to stress-critical applications like load-bearing railings or engine components.
Distinctive Production Perspectives: Rolling and Finishing
The production process imbues aluminum plate sheets with result-effective qualities. Plate sheets are traditionally produced via hot rolling—heating up aluminum billets and then cooling them by rolling under high pressure. This method not only refines structural grain patterns but also distributes stress across the surface, minimizing fatigue risk.
Additionally, the post-rolling surface finishing influences both aesthetics and functional wear-resistance:
-
Mill Finish: Characterized by a natural, slightly rough surface, it is preferred where subsequent treatment or strong mechanical bonding (like adhesive bonding) is required.
-
Polished or Brushed Finishes: Applied for architectural uses where visual appeal combines with protection from oxidation and environmental wear.
Why Aluminum Plate Sheets Excel Over Their Competitors
-
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Traditional steel plates can offer strength, but aluminum's significantly lower density delivers almost half or less of their weight, drastically reducing landed costs for transport and installation.
-
Extrinsic Corrosion Resistance: Unlike untreated steel, aluminum plate sheets quickly form a protective oxide layer when exposed to air. This attributes excellent resistance to rust and atmospheric degradation without requiring extensive external coatings.
-
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum plates provide a theoretical advantage where heat dissipation or lightweight electrical grounding is a aspect; crucial in electronic chassis design or heat exchangers.
-
Recyclability and Sustainability: Industry speculators strongly favor the fry melt recycling routes given aluminum’s ability to retain its material properties through multiple recycles.
Applications Benefitting from Aluminum Plate Sheets
-
Aerospace structures that demand rigid but lightweight components such as airframes and bulkheads
-
Vehicular bodies and panels where aerodynamic lightness helps fuel efficiency
-
Construction facades blending aesthetic metal alloys with outdoor durability
-
Industrial machinery plates that demand a balance of wear resistance and machinability
-
Cryogenic tanks and components, leveraging aluminum’s behavior at low temperatures without brittleness